Can a cheap IR Proximity Sensor on ESP32 really detect motion through plastic? I tested it.
There was a time I thought motion detection required a camera, a bulky sensor array, or at least a fancy dev kit. But one day, while rummaging through a box of leftover components from a community FOSS workshop, I found a tiny IR Proximity Sensor. Paired with an ESP32 and a handful of jumper wires, I wondered: Could this thing really detect motion through a plastic panel? That question turned into a late-night experiment—and a surprisingly effective low-cost solution for smart automation, all without relying on proprietary hardware or cloud services.
If you’re working on a project where budget, privacy, or simplicity matters, you’ll want to see how far you can take a humble IR Proximity Sensor and a $5 ESP32. Let me show you how.
What is an IR Proximity Sensor?
An IR proximity sensor detects objects by emitting infrared light and measuring the reflected signal. These sensors consist of an IR LED (emitter) and a photodiode or phototransistor (receiver). When an object is nearby, it reflects the emitted IR light, which the receiver detects. Based on the intensity of the reflected light, the sensor can determine the presence and, in some cases, the distance of the object.
Related:
Types of IR Sensors:
- Active vs. Passive: Active sensors emit IR light, while passive sensors detect ambient IR radiation.
- Reflective vs. Through-beam: Reflective sensors measure the reflection of light from objects, while through-beam sensors use a separate emitter and receiver to detect objects blocking the IR beam.
Applications include obstacle detection in robotics, line-following vehicles, and touchless automation systems.
Components Needed
To get started, you will need:
- ESP32 Development Board
- IR Proximity Sensor Module
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
- Optional: LED for output visualization
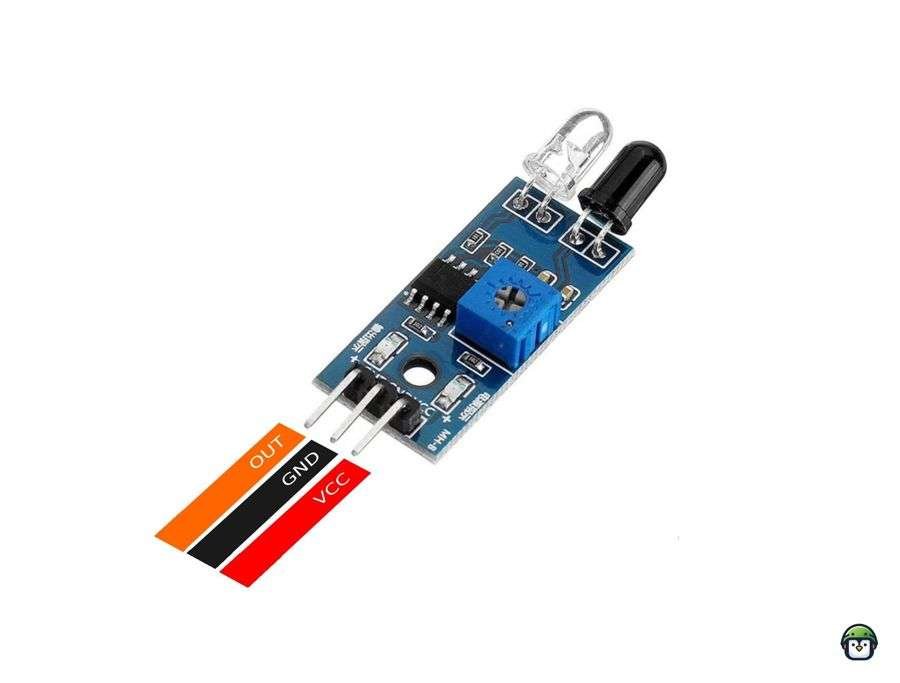
Wiring the IR Proximity Sensor with ESP32
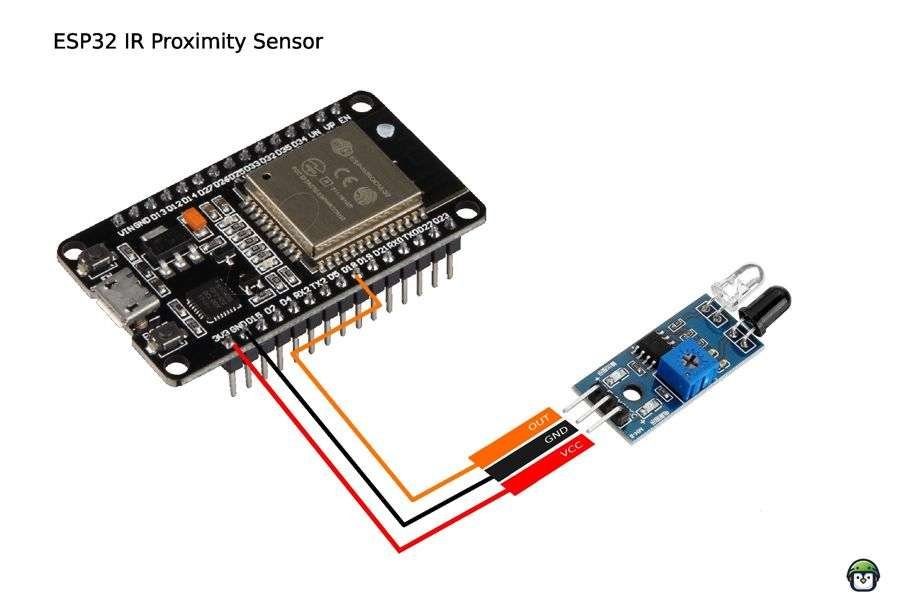
Connecting the IR proximity sensor to the ESP32 is straightforward. Here is the wiring guide:
- VCC: Connect to the 3.3V or 5V pin on the ESP32 (check your sensor’s voltage requirements).
- GND: Connect to the GND pin on the ESP32.
- OUT (Signal pin): Connect to a GPIO pin on the ESP32 (e.g., GPIO 18).
Programming the ESP32 with MicroPython
We will use MicroPython to program the IR proximity sensor ESP32 setup. If you haven’t set up MicroPython on your ESP32, follow a guide to install the firmware and use the Thonny IDE.
MicroPython Code Example
from machine import Pin
from time import sleep
# Initialize the sensor pin
ir_sensor = Pin(23, Pin.IN)
while True:
if ir_sensor.value() == 0:
print("Object detected!")
else:
print("No object detected.")
sleep(0.5)This script reads the sensor’s digital output and prints whether an object is detected. The Pin.IN configuration ensures the GPIO pin can read input signals from the sensor.
Testing and Calibration
- Testing: Upload the code to your ESP32 and open the serial monitor to view the sensor’s output. Place an object near the sensor and observe the changes.
- Calibration: Adjust the sensor’s potentiometer (if available) to fine-tune its detection range and sensitivity.
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Applications of IR Proximity Sensors with ESP32
Integrating an IR proximity sensor ESP32 setup enables a wide range of applications:
- Obstacle Avoidance in Robotics: Detect and avoid obstacles for autonomous navigation.
- Line-following Vehicles: Use the sensor to track lines on the ground.
- Touchless Automation: Create systems for automatic lighting, hand sanitizers, or door openers.
- Interactive Installations: Build responsive art or gaming setups.
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Smart Sensing, Open Tools
IR Proximity Detection That Just Works—No Frills, No Lock-In
You don’t need a corporate SDK or expensive hardware to make motion detection work. As you’ve seen, a basic IR Proximity Sensor and the ESP32 are more than enough to build reactive, low-power automation that’s entirely your own—from hallway lights to secret drawer triggers. With just a few lines of MicroPython and a little wiring patience, your DIY setups can rival commercial options—minus the surveillance and bloated firmware.
If you’re into free tools, small wins, and big ideas on a budget, I share more like this in my newsletter.
👉 Subscribe here for weekly field-tested ESP32 builds, FOSS hacks, and open automation tips:
https://www.samgalope.dev/newsletter/
Like what you’re reading?
Help keep DevDigest
free and caffeine-powered
—buy me a coffee on Ko-fi.





Leave a Reply