I tried Demucs on a lo-fi track—and it ripped the vocals cleaner than AI ‘premium’ tools.
If you’ve ever tried extracting vocals or instruments from a track, you know the struggle. Most tools leave behind ghostly echoes or muddy artifacts. But Demucs, an open-source AI-powered audio separator, changes the game. Developed by Meta, it doesn’t just remove vocals—it intelligently reconstructs high-quality stems, making it an essential tool for musicians, producers, and audio engineers.
No more hours spent tweaking EQ settings or wrestling with half-baked filters. Demucs uses deep learning to separate vocals, drums, bass, and other instruments with stunning clarity. Whether you’re remixing, creating karaoke tracks, or analyzing music composition, this tool delivers professional-grade results.
If you’re still using outdated methods to isolate vocals, you’re wasting time.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to install and use Demucs on your system, ensuring you get the best results from this open-source powerhouse.
🔥 Ready to transform the way you separate audio? Let’s dive in.
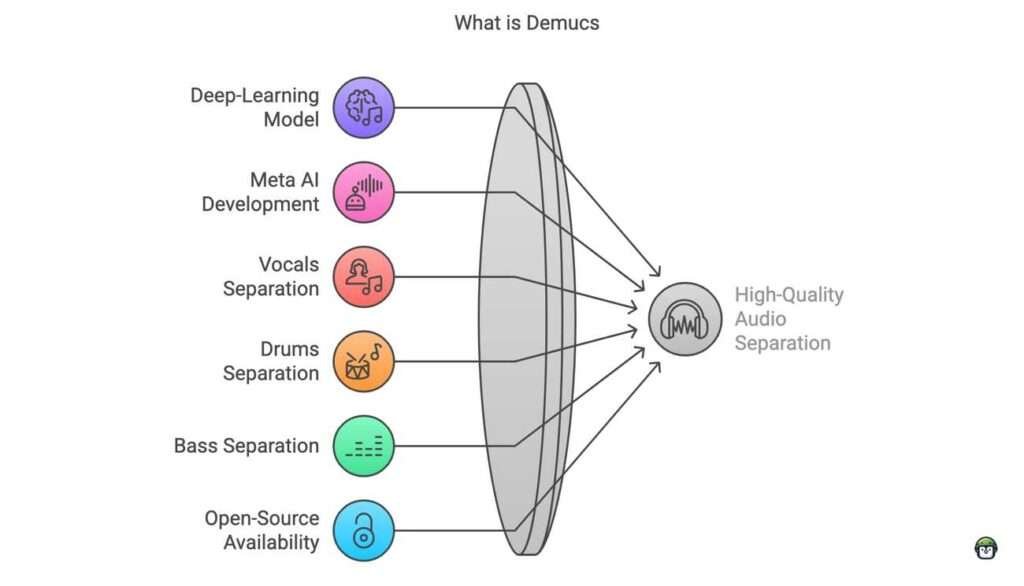
What is Demucs? A Powerful AI for Audio Separation
Demucs (Deep Extractor for Music Sources) is an open-source deep learning model designed to separate different elements of an audio track—such as vocals, drums, bass, and other instruments—into isolated stems. Developed by Meta (formerly Facebook AI Research), Demucs leverages recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and convolutional layers to achieve high-quality audio separation that rivals even commercial tools.
Unlike traditional FFT-based (Fast Fourier Transform) separation methods, which often produce robotic-sounding artifacts, Demucs reconstructs waveforms in a more natural and expressive way. This makes it a favorite among musicians, producers, and audio engineers looking for clean and accurate instrument separation.
Why Use Demucs?
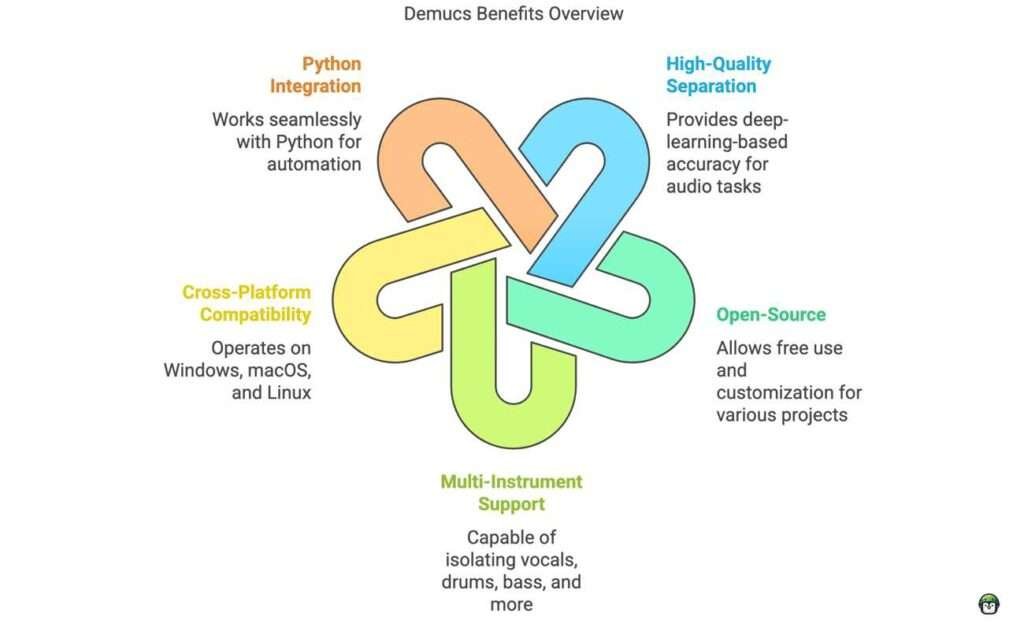
- High-Quality Separations: The deep learning model behind Demucs offers better precision and clarity than traditional audio separation techniques, minimizing artifacts and distortions.
- Open-Source and Community Driven: As an open-source project, Demucs is freely accessible and constantly improved by a community of contributors, ensuring cutting-edge performance.
- Cross-Platform Support: Demucs can be used on various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, and can be integrated into different workflows via the command line.
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
How Demucs Works
Demucs processes audio input through a convolutional neural network designed to separate sound into multiple channels based on frequency patterns and timing. These channels correspond to specific components like vocals, bass, or drums. The tool outputs these components as individual audio files, which can then be modified, mixed, or analyzed independently.
The network is trained on large datasets comprising diverse genres to ensure it performs effectively on both popular and niche music styles. This versatility makes it a popular tool among a wide range of users, from casual enthusiasts to professional producers.
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Key Use Cases of Demucs
- Music Production and Remixing:
Demucs allows producers to isolate vocals, drums, or other instruments from existing tracks, providing the raw elements necessary to remix or build new music from pre-recorded works. DJs can also extract specific components, such as acapella vocals or drum loops, for use in live performances or mashups. - Karaoke Track Creation:
By extracting the vocal component of a song, Demucs can generate instrumental-only tracks that are perfect for karaoke enthusiasts or practice sessions for musicians. - Educational and Analytical Purposes:
Music students and analysts can use Demucs to study the arrangement of individual elements in a piece, better understanding the interplay between instruments, rhythms, and harmonies. - Audio Restoration and Forensics:
Demucs can assist in audio forensics or restoration projects, where isolating certain elements (such as background music) from a recording is needed for analysis or enhancement.
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Prerequisites
Before we start, ensure you have the following installed on your system:
- Python 3.6 or later: You can download it from the official Python website.
- Demucs: This can be installed using pip.
- FFmpeg: A tool required for audio processing. You can download it from the FFmpeg website.
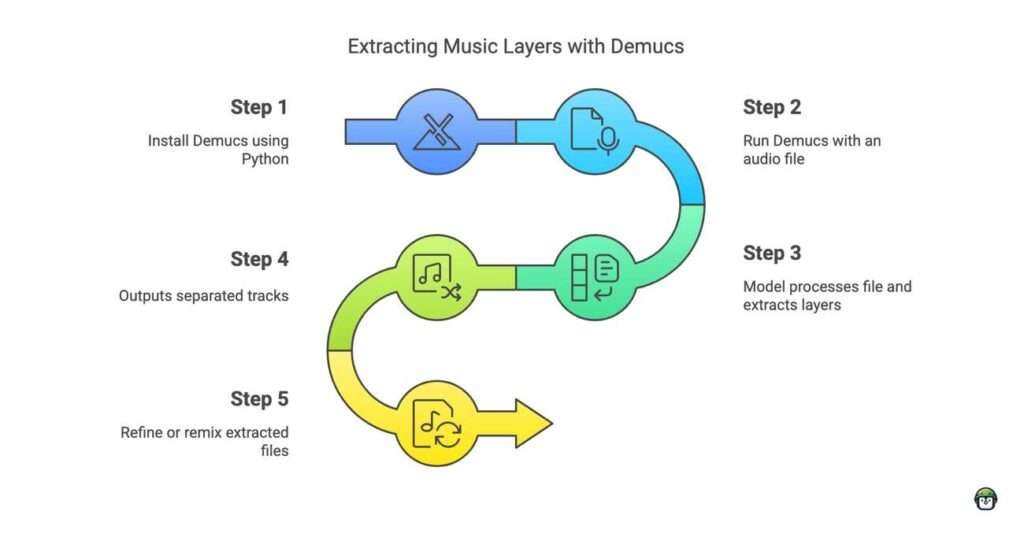
Step 1: Install Demucs
First, let’s install Demucs and its dependencies. Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
pip install demucsUpdate: As of Nov 3, 2024, I have been having problems installind demucs on my machine. I tried installing directly from githhub to no avail. I also tried purging the pip cache, no cigar. Here’s the solution.
python3 -m pip install -U demucsStep 2: Prepare Your Audio File
Ensure your audio file is in a compatible format (e.g., MP3, WAV). For this example, we’ll assume you have an MP3 file named song.mp3.
Step 3: Use Demucs to Separate the Audio
Create a Python script named separate_audio.py and add the following code:
# Ensure FFmpeg is available
os.system("ffmpeg -version")
# Command to run Demucs
command = "demucs --mp3 song.mp3"
# Execute the command
os.system(command)This script uses the os module to execute shell commands. The demucs --mp3 song.mp3 command tells Demucs to process song.mp3 and output the separated components.
Step 4: Run the Script
Execute your script by running the following command in your terminal:
python separate_audio.pyDemucs will process the audio file and create separate files for each component (vocals, drums, bass, and other) in a new directory named separated.
Step 5: Verify the Output
Navigate to the separated directory to find the processed audio files. You should see something like this:
separated/
└── song/
├── vocals.wav
├── drums.wav
├── bass.wav
└── other.wav· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Additional Options
Demucs offers various options for customization. For example, you can specify a different model or change the output format. To see all available options, run:
$ demucs --help· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Handling NumPy Compatibility Issues
If you encounter an issue where a module compiled with NumPy 1.x cannot run in NumPy 2.0.1, you need to either downgrade NumPy or rebuild the module. Here’s how to do it:
Downgrade NumPy
Uninstall Current NumPy Version:
$ pip uninstall numpyInstall Compatible NumPy Version:
$ pip install 'numpy<2'· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
· · ─ ·𖥸· ─ · ·
Open-Source Audio Magic, One Command at a Time
Demucs may sound like science fiction—but it’s real, reproducible, and ridiculously effective. You’ve just seen how to use Demucs to break down full tracks into clean, usable stems, using nothing more than Python and the command line.
Whether you’re remixing, analyzing, or just having fun, tools like Demucs show what’s possible when FOSS meets machine learning—no subscriptions, no surveillance, no strings attached.
If this kind of practical open-source magic speaks to you, let’s keep in touch.
👉 Subscribe to the DevDigest Newsletter for more no-fluff guides that help you build, break, and remix the world—one line of code at a time.






Leave a Reply